
Longevity – Living healthily and growing old – the secret of success of longevity
Reading time: 5 minutes
Contents
Who doesn't want to stay vital and healthy into old age? Studies show that despite our genetic basis, we have many aspects of aging in our own hands. The longevity trend is based on a healthy lifestyle that goes far beyond genetic predisposition . With the right diet, exercise and stress management, aging can be positively influenced. In this article, you'll find out exactly how this works and how you can integrate it into your everyday life.
What does longevity mean?
The term "longevity" describes the ability to live a healthy and vital life beyond the average life expectancy . There are already many people who live well into their 80s, but the price of reaching this age is often high. Severe physical limitations, chronic pain and a long list of medications are often part of everyday life. As part of the longevity trend, more and more people are actively looking for ways to maintain their quality of life into old age. Longevity is therefore not just aimed at a long life , but also at aging as healthily and fulfilled as possible.
Stay healthy longer thanks to 6 important longevity factors
1) Nutrition – the basis of longevity
"You are what you eat" - this well-known phrase aptly sums up how strongly our diet influences our health and longevity. Because: A balanced diet plays a central role in longevity. A plant-based diet in particular, rich in fresh vegetables, fruit, whole grain products, pulses and nuts, has been proven to have positive effects on health and can prevent age-related diseases. While fish provides valuable omega-3 fatty acids , you should limit your consumption of red meat, sugar and highly processed foods. Because these increase the risk of chronic diseases and can have a negative impact on longevity .
How Intermittent Fasting Relieves the Body
In addition to the nutrient intake, the amount of calories you consume daily also plays an important role. Studies show that reducing calories can reduce the risk of age-related diseases. In this context, interval fasting has proven to be particularly effective. Here, you skip certain meals, which relieves the body and stimulates your cells to regenerate.
Does a change in diet still make any difference in old age?
A change in diet is sensible at any stage of life - but the earlier healthy habits are established, the greater the benefit for one's own lifespan and quality of life. Those who start early can do more for their health in the long term and benefit most from the positive effects. A healthy diet, combined with regular phases of calorie reduction, creates the basis for a long and vital life. But exercise is also an important factor!
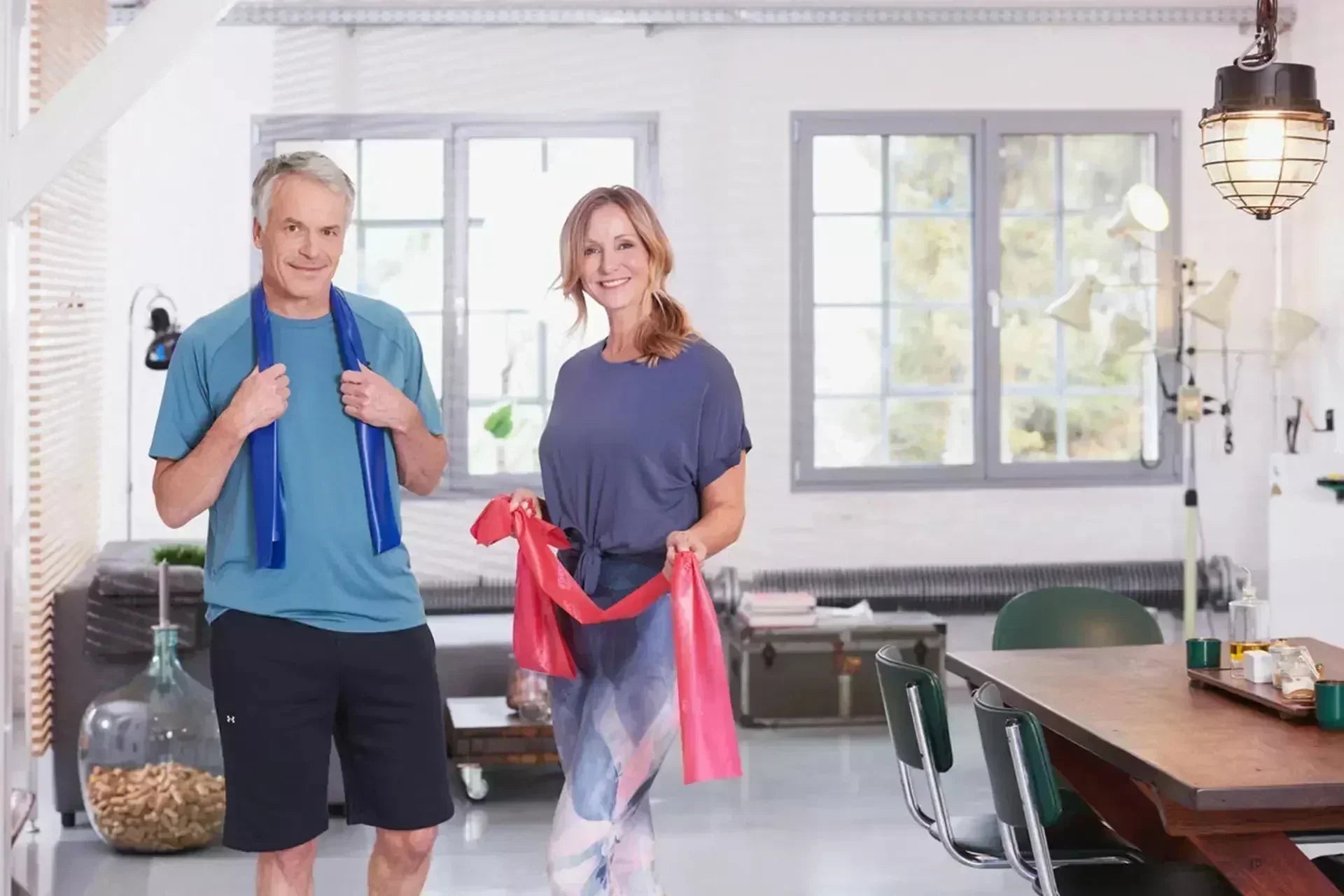
2) Exercise and fitness: Live longer and be active
Did you know that the often-mentioned 10,000 steps a day have never been scientifically proven? Researchers found that just 4,400 to 7,500 steps a day are enough to have a positive effect on longevity. Studies also show that daily walking is one of the simplest and most effective ways to improve your health in the long term and extend your life. Just 150 minutes of moderate exercise a week - about two and a half hours - can make a big difference. In general, every movement counts - whether it's endurance training for your heart or strength training for strong muscles.

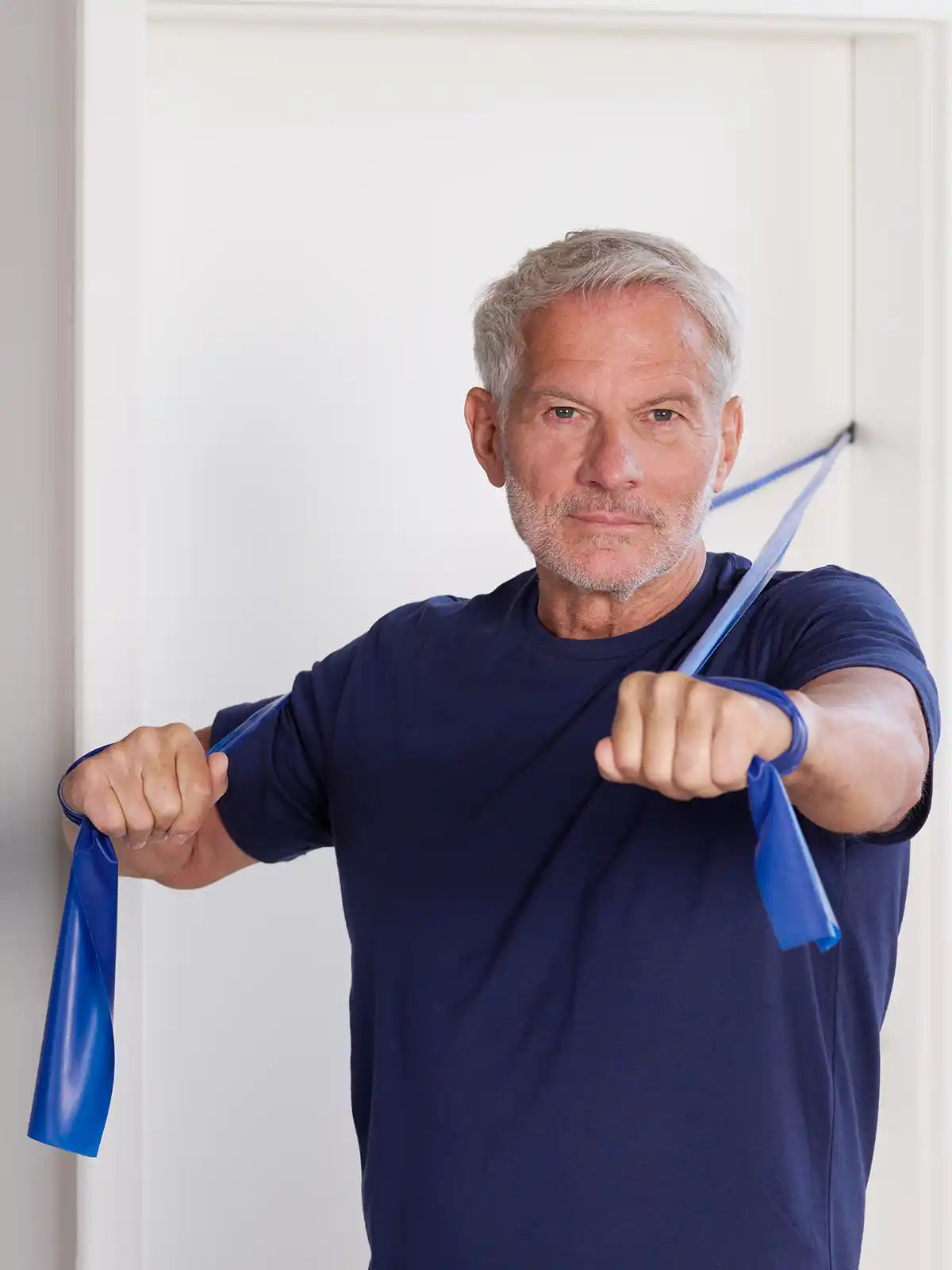
Tip: A TheraBand is particularly practical and versatile. This simple fitness tool offers you resistance training that is gentle on your joints and is perfectly suited to any age and fitness level. Whether you are at home or on the go, the flexible exercises with the TheraBand promote strength and mobility and help you to actively improve your longevity!
3) Sleep and rest: regeneration for body and mind
Sleep is your secret weapon for health and well-being. If you get enough sleep regularly, you give your body and mind the chance to regenerate properly . Do you often have trouble sleeping? Try to stick to set times and turn your bedroom into a screen break zone. If stress is keeping you awake, relaxation techniques such as meditation or breathing exercises can help you calm down. Good sleep means more energy, a better mood and a stronger immune system. Your body will thank you!
4) Social contacts and mental health: living longer through community
Did you know that social contacts also have an impact on longevity? People who live in a strong community often stay fit and healthy for longer. Social contacts can also be combined with other areas of life. Being active together, for example playing sports or going for walks with friends, perfectly combines fitness and social interaction . This not only strengthens your body, but also your mind. So grab your friends, keep moving and benefit twice over - for more joy in life and a longer life!
5) Avoid harmful habits: limit smoking and alcohol
If you really want to improve your longevity, it is important to limit harmful habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Nicotine damages the heart and lungs, alcohol puts a strain on organs such as the liver and increases the risk of many diseases. Studies show that those who give up smoking and drinking too much alcohol can extend their lifespan by years . Of course, you don't have to change everything immediately, but every step in this direction will bring you better health and quality of life.
6) What role do genes play in a long life?
Many people think that our age is determined by our genes, but that is only about 10-15% true. Much more important is the lifestyle we lead and the environmental influences we are exposed to. Studies show that people within a family often live to a similar age because they live similarly. Although there are genetic risk factors, such as a predisposition to Alzheimer's or cardiovascular disease, around 85-90% of our lifespan is in our own hands . With a healthy diet, exercise, etc., you can do a lot for your longevity!
Research and Innovations on Longevity
More and more people don't just want to look young, but also want to stay fit and healthy into old age. Research into longevity is constantly producing new approaches - from cell rejuvenation to blood plasma therapy. Scientists are also looking at so-called blue zones, regions in which people live to a particularly old age and remain particularly healthy. The lifestyle there, characterized by exercise, a plant-based diet and social cohesion, provides valuable insights. Technologies such as the "reprogramming" of cells could slow down aging in the future and significantly increase our lifespan. The future of longevity therefore remains exciting!
Conclusion: Longevity as a lifestyle
Longevity is not a coincidence, but the result of conscious, responsible decisions in everyday life. Through a healthy diet, regular exercise and avoiding harmful habits, you can actively improve your lifespan and quality. It is often small changes that can make a big difference . Start today with simple steps and make your life more active and healthier in the future - for many happy years!
You will surely find this exciting too:
Simple TheraBand exercises to keep fit from home >
Breathing training – tips and exercises for more health and performance >
Digital Overload: Strategies to combat stress in everyday digital life >
Sources
Can We Say What Diet Is Best for Health?
Caloric restriction
JAMA Internal Medicine: Association of Step Volume and Intensity With All-Cause
Mortality in Older Women
DHS – Recommendations for dealing with alcohol
Old plasma dilution reduces human biological age: a clinical study
Metabolic Slowing and Reduced Oxidative Damage with Sustained Caloric Restriction Support the Rate of Living and Oxidative Damage Theories of Aging
Impact of intermittent fasting on health and disease processes
The brain structure and genetic mechanisms underlying the nonlinear association between sleep duration, cognition and mental health
WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behavior




Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.